
Summary
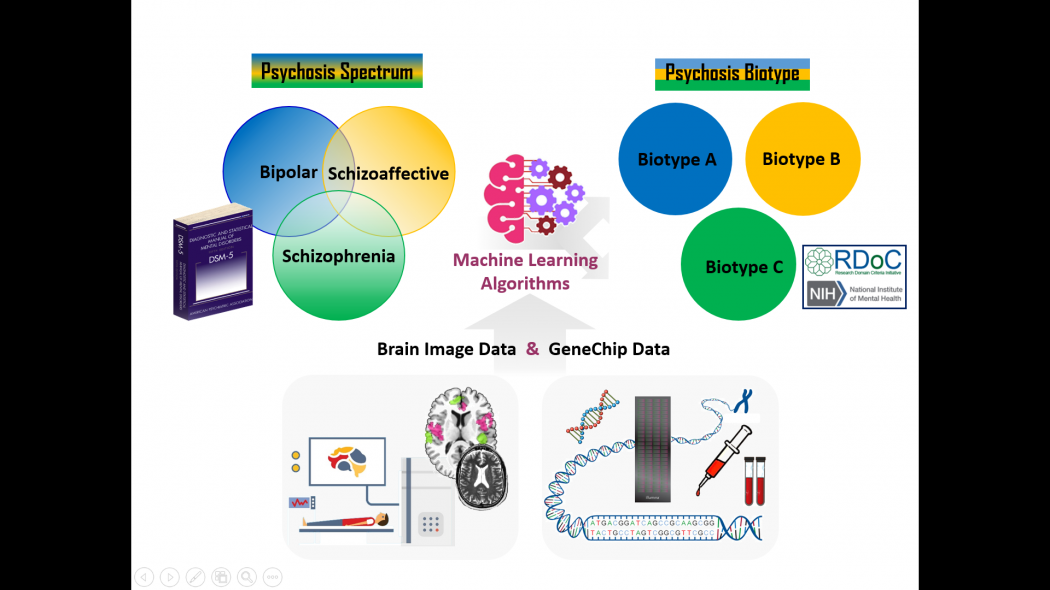
Increasing amount of neuroimaging and genetic data has been established in recent years to understand the complex brain functions in both healthy and pathologic mental conditions. To quantify the complex brain signal data, an approach that integrates mathematics, physics, and computational neuroscience is required. Therefore, we aim to develop the Research Domain Criteria (RDoC) strategy with machine learning-based computational algorithms to phenotype psychotic spectrum disorders. The project has adopted the data from Taiwan Mental Illness Cohort, Bipolar and Schizophrenia Network for Intermediate Phenotypes and Harvard Brain Genomic Superstruct Project to establish the Brain Atlas for Neuropsychiatric Disorders.
Applications
A computational framework based on the RDoC approach to quantify biological classifications of psychotic spectrum disorders by incorporating developed brain imaging and genetic markers will be provided. Up to date, we have used deep neural networks with fMRI data to classify schizophrenia, and with structural MRI for multi-class classification (schizophrenia, bipolar disorder and healthy control). In addition, we have identified the genome-wide associations in brain images with machine learning techniques. Combining the data retrieved from NHI, we used ResNeXt100 to classify subtypes of Intracranial Hemorrhage with 97.7% accuracy.
Advantages
We anticipate identifying the biological classification of psychiatric disorders that was based on differentiation of complexity markers in different brain regions across psychotic spectrum disorders. We also expect that such biological classification of psychosis may have better clinical differentiation than DSM diagnoses based on taxonomic approaches.
Related Links
Laboratory of Precision Psychiatry (http://www.psynetresearch.org/)
Keywords
Psychiatric disorders; machine learning; neuroimaging; genomic
◎ PI

PI Shih-Jen Tsai
Chief, Department of Psychiatry, Taipei Veterans General Hospital

Co-PI Chih-Chieh Yang
Attending Psychiatrist, Department of Psychiatry, Taipei Veterans General Hospital

Co-PI Weichung Wang
Professor, Graduate Institute of Applied Mathematical Sciences, NTU

Co-PI Su-Yun Chen
Research Fellow, Institute of Statistical Science, Academia Sinica

Co-PI Ting-Li Chen
Associate Research Fellow, Institute of Statistical Science, Academia Sinica
[July 5th, 2021] Paper accepted by international journal Frontiers in Psychiatry !
Development of an Al-Based Web Diagnostic System for Phenotyping Psychiatric Disorders
Frontiers in Psychiatry. 2020 Nov 5;11:542394.
https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpsyt.2020.542394/full
(This is an Open Access paper, click the link to read fulltext for free.)
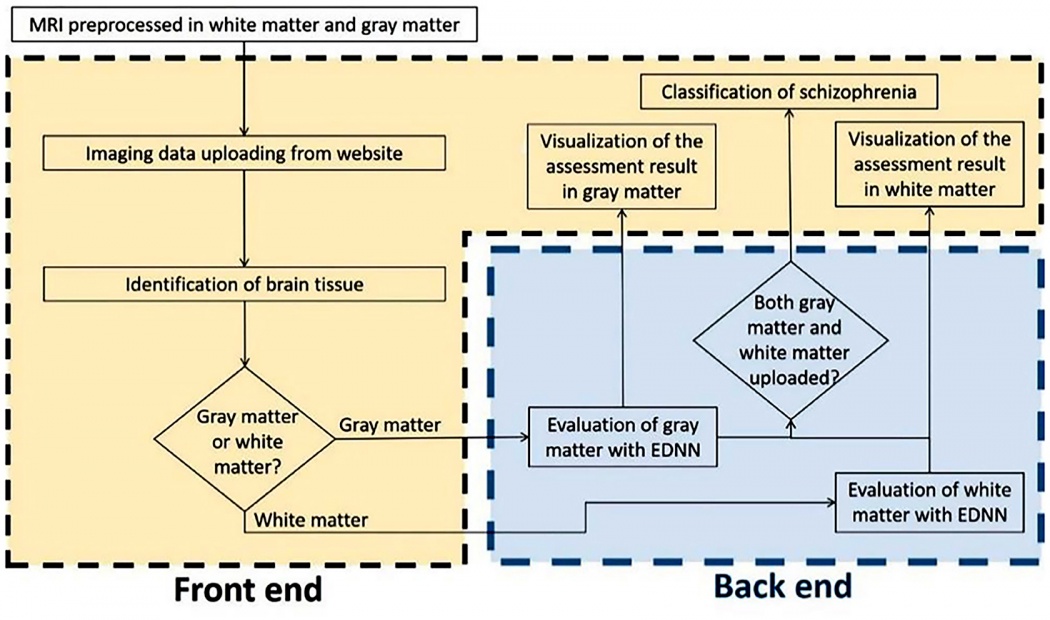
Artificial intelligence (AI)-based medical diagnostic applications are on the rise. The current AI-based web diagnostic system consisted of a web server and a neuroimaging diagnostic database. Feature selection and network model building were performed on the dataset obtained from two hundred schizophrenic patients and healthy controls in the Taiwan Aging and Mental Illness cohort, and achieved 84.00% accuracy for gray matter and 90.22% accuracy for white matter. Our system is also featuring a powerful visualization to the identified voxels in brain atrophy in a three-dimension manner with patients' structural image, optimizing the evaluation process of the diagnostic results. Here, we demonstrated the potential future direction of making a schizophrenia diagnosis based on structural brain imaging data. Our deep learning model is explainable, arguing for the accuracy of the key information related to the pathology of schizophrenia when using the AI-based web assessment platform.

[2020/01/14] "AI-based Web Diagnostic System for Assessing Psychiatric Disorder" awarded with "Best Popular Tech Award" at 2019 Future Tech!


Introduction of the Technology: Mental illness is a critical health care issue in Taiwan. Psychiatric diagnosis has been relied on diagnostic interview which is based on behavioral or symptom criteria. The emergence of brain imaging diagnostic platform can efficiently improve the accuracy of psychiatric diagnosis! Furthermore, this platform can identify the deficit brain regions associated with schizophrenia, providing a novel way to evaluate mental illness.
This technique is led by Dr. Albert C. Yang at Institute of Brain Science/Digital Medicine Center at National Yang Ming University and Dr. Shih-Jen Tsai at Taipei Veterans General Hospital. The AI-based schizophrenia brain imaging diagnosis can be a new tool for medical psychiatrist. Our team utilized brain imaging and genomics big data to develop an explainable deep learning classifiers. Users can simply upload routine MRI brain images to our platform to obtain clinically useful diagnostic information, which could aid medical doctor for diagnostic evaluation and treatment options.
Additionally, this platform cannot only provide schizophrenia assessment but also to visualize the brain regional deficit associated with schizophrenia. Through this way, we could improve the clinical work flow to be more clear and straightforward. This web-based diagnostic platform has been validated in a multi-centers trial.




